Tech
tech homePin 9 - Gray. The function of each pin will depend on what signaling standard you are using. I am also unsure if these colors are ubiquitous, or if it just a standard that is typically followed.
web stuff
dom stuff
css stuff
language stuff
regex stuff
rfc stuff
protocol stuff
cable stuff
lan wiring
rs232 wiring
howto stuff
wireless stuff
ascii codes
data rate stuff
telephony stuff
mechanical stuff
pc stuff
electronic stuff
tech links
open guides
RS232 Wiring Stuff
RS232 standards are defined by EIA/TIA (Electronic Industries Alliance/Telecommunications Industry Association). RS232 defines both the physical andelectrical characteristics of the interface. RS232 is practically identical to ITU V.24(signal description and names) and V.28 (electrical). RS232 is an Active LOW voltage driven interface andoperates at +12V to -12V where:
Signal = 0 (LOW) > +3.0V
Signal = 1 (HIGH) < -3.0V
Notes:
- Signal voltages in the range >-3.0V to +3.0V is regarded as the 'dead area' and allows for absorption of noise. For more on the use of signals and other heavy stuff.
- The power level on RS232 pins is defined by TIA in terms of short circuit protection to be 100mA. Most RS232 drivers will provide lower short circuit protection (especially for laptops). A max of 50mA PER PIN may be available but the data sheet for the specific interface/chip should be consulted before commiting to externally powered designs.
- We received an email recently pointing out some issues with NULL modem cables. The pinouts shown below will gnerally work. However there are many permutations of signal sets that can be used by either end of a connection and they may not be SYMMETRIC. One end may expect something (a signal) that the other end cannot generate. This typically happens with CTS/RTS (and perhaps DCD) and DTR/DSR. If you suspect this is the case then unfortunately you need to UNDERSTAND the interface and may have to SPOOF certain signals. Our signal primer page may help you. Finally if you are having serious problems, splash out on a light box or some other device that will show you which signals are being activated.
- Watch the terms DTE (Data Terminal Equipment - a terminal or PC) and DCE (Data communications Equipment - for example, a modem) the meaning and use of certain pins may differ. All the diagrams below define the interface from the DTE perspective. An RS232 interface has a female and male connector, the male connector has the bits sticking out!!
- The terms Data Carrier Detect (DCD) and Received Line Signal Detect (RLSD) are one and the same. We use DCD throughout 'cos we think it's more common.
- Like most folks we use the term DB9 which is widely - but erroneously - used to describe a 9-pin serial connector. We got an email pointing out the error of our ways. So, if you want to amaze your friends over the dinner table you can read more here and use the technically correct terms in the future. While we get away with it most of the time (with common or garden PCs), sometimes it is essential to know EXACTLY what connector type you are talking about.
- RS-232-E is normally defined to be used with a DB25 connector, but does have a 26 pin (a much smaller connector) alternate . We suggest that if you come across one of these that you do the decent thing - use an expletive. Alternatively, with your luck, you could consider buying a lottery ticket.
- We have received a number of emails recently asking how to wire DB9's using cat5(e) cable. We guess there is a lot of LAN cable lying around these days so folks naturally want to use it. We have added a null modem only section to cover this wiring. There is absolutely no standard to cover this form of wiring. This section is simply offered as one of many possible ways to do it.
Contents
RS232 on DB25 (RS-232C)
Note: This is NOT the same as the DB25 Parallel port on a PC.
| Pin No. | Name | Notes/Description | Pin No. | Name | Notes/Description |
| 1 | - | Protective/shielded ground | 14 | STD | Secondary Transmit Data |
| 2 | TD | Transmit Data (a.k.a TxD, Tx) | 15 | DB | Transmit Clock (a.k.a TCLK, TxCLK) |
| 3 | RD | Receive Data (a.k.a RxD, Rx) | 16 | SRD | Secondary Receive Data |
| 4 | RTS | Request To Send | 17 | DD | Receive Clock (a.k.a. RCLK) |
| 5 | CTS | Clear To Send | 18 | LL | Local Loopback |
| 6 | DSR | Data Set Ready | 19 | SRTS | Secondary Request to Send |
| 7 | SGND | Signal Ground | 20 | DTR | Data Terminal Ready |
| 8 | CD | Carrier Detect (a.k.a DCD) | 21 | RL/SQ | Signal Quality Detector/Remote loopback |
| 9 | - | Reserved for data set testing | 22 | RI | Ring Indicator (DCE raises when incoming call detected used for auto answer applications) |
| 10 | - | Reserved for data set testing | 23 | CH/CI | Signal Rate selector |
| 11 | - | Unassigned | 24 | DA | Auxiliary Clock (a.k.a. ACLK) |
| 12 | SDCD | Secondary Carrier Detect | 25 | - | Unassigned |
| 13 | SCTS | Secondary Clear to send | - | - | - |
NOTE: Leave all pins not specified above unconnected.
view - looking into male connector
RS232 on DB9 (EIA/TIA 574)
| Pin No. | Name | Notes/Description |
| 1 | DCD | Data Carrier Detect |
| 2 | RD | Receive Data (a.k.a RxD, Rx) |
| 3 | TD | Transmit Data (a.k.a TxD, Tx) |
| 4 | DTR | Data Terminal Ready |
| 5 | SGND | Ground |
| 6 | DSR | Data Set Ready |
| 7 | RTS | Request To Send |
| 8 | CTS | Clear To Send |
| 9 | RI | Ring Indicator |
View - looking into male connector
RS232 on RJ45 (RS-232D)
More properly EIA/TIA - 561. Use when connecting to or from a serial port with a 8 position Modular Jack (RJ45). If you are cross-connecting from a DB9 or a DB25 use the signal names to cross connect the appropriate connections.
| Pin No. | Name | Notes/Description |
| 1 | DSR/RI | Data set Ready/ring indicator |
| 2 | DCD | Data Carrier Detect |
| 3 | DTR | Data Terminal Ready |
| 4 | SGND | Signal Ground |
| 5 | RD | Receive Data |
| 6 | TD | Transmit Data |
| 7 | CTS | Clear to Send |
| 8 | RTS | Request to Send |
Note: Pin 1 is a multi-function pin sharing with DSR (Data Set Ready) and RI (Ring Indicator). This means it is impossible to differentiate between a incoming ring signal and when the modem has finally connected and synched up. With local (null modem connections) or if the modem is run in auto-answer mode this is not normally a problem. If used with a modem and the DTE (the computer end) wants to control the connection the problem is more real. DSR would normally indicate the 'connected and synched-up' state following DTR from the DTE. DCD will indicate that a carrier has been received but does not indicate synchronization of both ends. In most cases however CTS (Clear To Send) in response to RTS (Request To Send) will not normally be returned until an end-to-end connection is available.
RJ45 Male Connector Pin Numbering
RS232 DB25 NULL Modem Pinout
Use when connecting two systems (e.g. PCs) via their DB25 interfaces without a modem (i.e. back-to-back). See the full signal names in the DB25 sections.
If this pinout does not work for you then you could try our Signal/pin primer because you may need to SPOOF connections.
Note: This DB25 is NOT the same as the DB25 Parallel port on a PC which is defined here.
| DB25 | Signal | DB25 | Signal |
| 3 | RD | 2 | TD |
| 2 | TD | 3 | RD |
| 20 | DTR | 6,8 | DSR, DCD |
| 6,8 | DSR, DCD | 20 | DTR |
| 4 | RTS | 5 | CTS |
| 5 | CTS | 4 | RTS |
| 7 | SGND | 7 | SGND |
| 22 | RI | 22 | RI |
View - looking into male connector
NOTE:
- Leave all pins not specified above unconnected.
- We have received email suggesting that the above pinout looks like DTR from one side is driving into DSR/DCD on the other side - not normally a healthy situation. The emails miss the point that since both ends are DTEs NEITHER should be attempting to drive the DSR/DCD signals. They are essentialy RX only signals on both sides.
RS232 DB9 NULL Modem Pinout
Use when connecting two systems (e.g. PCs) via their DB9 interfaces without a modem (i.e. back-to-back). See the full signal names in the DB9 section.
If this pinout does not work for you then you could try our Signal/pin primer because you may need to SPOOF connections.
| DB9 | Signal | DB9 | Signal |
| 2 | RD | 3 | TD |
| 3 | TD | 2 | RD |
| 4 | DTR | 6,1 | DSR, DCD |
| 6,1 | DSR, DCD | 4 | DTR |
| 7 | RTS | 8 | CTS |
| 8 | CTS | 7 | RTS |
| 5 | SGND | 5 | SGND |
| 9 | RI | 9 | RI |
View - looking into male connector
NOTE:
- We have received email suggesting that the above pinout looks like DTR from one side is driving into DSR/DCD on the other side - not normally a healthy situation. The emails miss the point that since both ends are DTEs NEITHER should be attempting to drive the DSR/DCD signals. They are essentialy RX only signals on both sides.
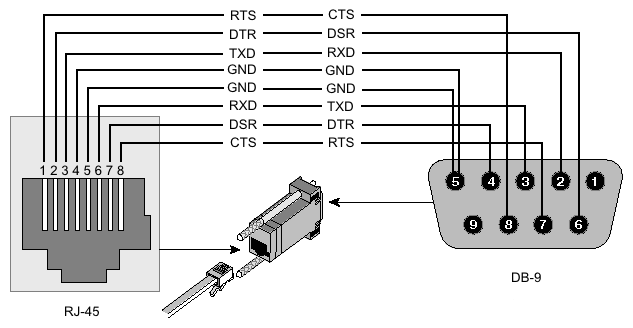
RS232 DB9 NULL Modem Pinout on CAT5
This is in response to a number of recent emails asking how to wire both ends of a DB9 connection using cat5(e) cable. This must not be confused with DB9 to RJ45 (RS232D). We have shown a null modem (back-to-back PCs) only configuration. And if you want to use cat5(e) with a real modem (a DB25 connector)? Our advice - don't.
Warning:. There is, as far as we know, no standard to cover the use of cat5(e) (8 conductor) wiring when used with two DB9 connectors. Any such wiring scheme is therefore non-standard - that includes the wiring scheme below. Specifically this means that both ends of the cable must be wired in the same way and that no assumptions can be made about how the other end is wired. You will have to manually inspect both ends of the connection. Damage can result from mis-matched wiring.
A DB9 clearly has 9 connections and a cat5(e) cable has 8 conductors. RS232D has chosen to use Pin 1 as a multi-function pin (DSR/RI) to provide maximum flexibility with modems - in particular it allows for DCD which is a meaningful signal from a modem but not we suggest from a peer PC. We have chosen to use a minor variation on the normal DB9 Null modem pinout above - specifically we have allowed for RI which could be used from a peer PC to commence a transmission sequence. The actual colors are unimportant but the suggested configuration is one way to provide the shortest use of the adjacent (twisted) pairs.
If this pinout does not work for you then you could try our Signal/pin primer because you may need to SPOOF connections.
| PC1 Peer | PC2 Peer | ||||
| DB9 | Signal | cat5(e) Color | DB9 | Signal | cat5(e) Color |
| 2 | RD | Brown | 3 | TD | Blue |
| 3 | TD | Blue | 2 | RD | Brown |
| 4 | DTR | Green | 6,1 | DSR, DCD | Brown-white |
| 6,1 | DSR, DCD | Brown-white | 4 | DTR | Green |
| 7 | RTS | Blue-white | 8 | CTS | Green-white |
| 8 | CTS | Green-white | 7 | RTS | Blue-white |
| 5 | SGND | Orange | 5 | SGND | Orange |
| 9 | RI | Orange-white | 9 | RI | Orange-white |
View - looking into male connector
NOTE:
- We have received email suggesting that the above pinout looks like DTR from one side is driving into DSR/DCD on the other side - not normally a healthy situation. The emails miss the point that since both ends are DTEs NEITHER should be attempting to drive the DSR/DCD signals. They are essentialy RX only signals on both sides.
RS232 DB9 to DB25 Pinout
Use when connecting a DB9 (e.g. a PC) to a DB25 (e.g. a modem) interface. See the full signal names in the DB9and DB25 section.
| DB9 | Signal | DB25 |
| 1 | DCD | 8 |
| 2 | RD | 3 |
| 3 | TD | 2 |
| 4 | DTR | 20 |
| 5 | SGND | 7 |
| 6 | DSR | 6 |
| 7 | RTS | 4 |
| 8 | CTS | 5 |
| 9 | RI | 22 |
View - looking into male connector

View - looking into male connector
NOTE: Leave all pins not specified above unconnected.
RS232 DB9 to DB25 NULL Modem Pinout
Use when connecting two systems (e.g. PCs) when one has a DB9 interface and the other a DB25 interface without a modem (i.e. back-to-back). See the full signal names in the DB9and DB25 sections.
| DB9 | Signal | DB25 | Signal |
| 2 | RD | 2 | TD |
| 3 | TD | 3 | RD |
| 4 | DTR | 6,8 | DSR, DCD |
| 6,1 | DSR, DCD | 20 | DTR |
| 7 | RTS | 5 | CTS |
| 8 | CTS | 4 | RTS |
| 5 | SGND | 7 | SGND |
| 9 | RI | 22 | RI |
View - looking into male connector
